2. a. Describe how the kidney removes metabolic wastes from the body. [7]
b. Man can produce urine which is more concentrated than their blood plasma. Explain the role
of the loop of Henle in the reabsorption of water from filtrate. [8]
Answer:
2.a.

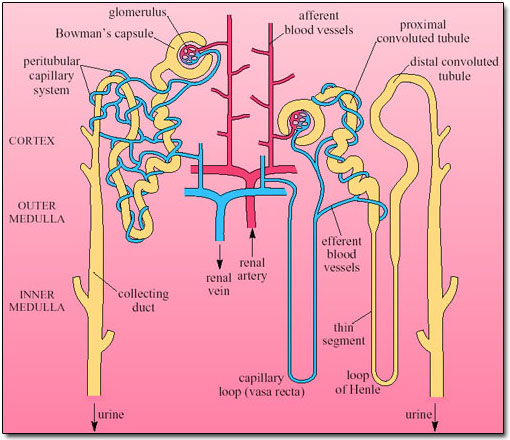

- ultrafiltration
- of blood in glomerulus ;afferent arteriole bigger in diameter than efferent arterioles,high hydrostatic
pressure created
- forming filtrate in Bowman's capsule
- reabsorption
- soluble molecules ;glucose,amino acids ,urea , ammonium ions pass into filtrate
- the metabolite waste are ammonia salts creatine, excess water sodium& chloride ions
- in proximal convoluted tubule 80% of water and NaCl is reabsorbed
- In the loop of henle,Na+ move out of ascending limb into medulla tissue
- This cause reabsorbtion of H2O from descending
- limb
-The remaining salt is reabsorb in the distal convoluted tubule and the H2O is reabsorb in the distal
tubule and collecting duct.
-Active Secretion
-The urea is actively secreted into the tubule from the surrounding capillaries
2. b.

- In the ascending limb sodium(ions) actively removed in the medulla tissue
- Ascending limb impermeable to water
- In descending limb sodium(ions) diffuse in
- Descending limb water moves out/permeable to water
- Low water potential/high concentration of ions in the medulla/tissue fluid
- The longer the loop/the deeper into medulla, the lower the water potential in medulla/tissue fluid
- Water leaves collecting duct/DCT
- By osmosis/down water potential gradient









